Significance
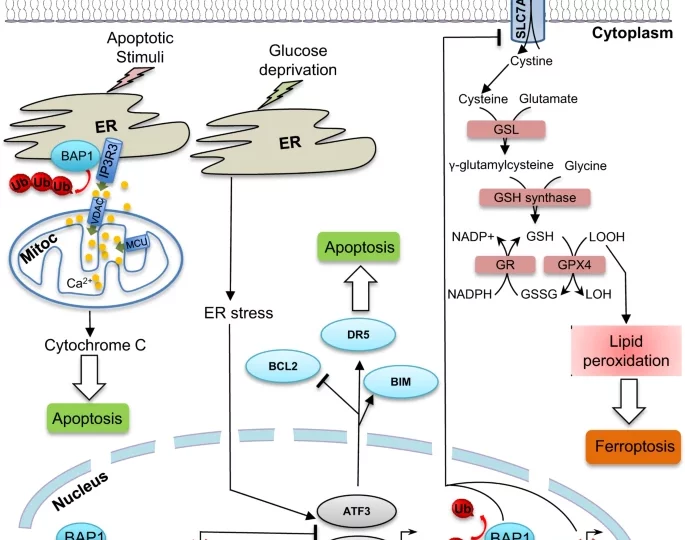
The ubiquitin carboxyl terminal BAP1 is a member of deubiquitinating enzymes superfamily, which are responsible for coordinating ubiquitin-signaling processes through the removal of ubiquitin from protein substrates. Studies of families with high incidence of mesothelioma led to the discovery that all affected family members carried heterozygous BAP1 mutations (BAP1+/−), a condition that was named “the BAP1 cancer syndrome”.
Since the initial discovery in 2011, over 100 families have been identified worldwide affected by the BAP1 cancer syndrome.
El Bachir Affar, Michele Carbone
Nature
December 12, 2018 | doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-1206-5

